Image Segmentation with Weak Supervision
Technologies Used
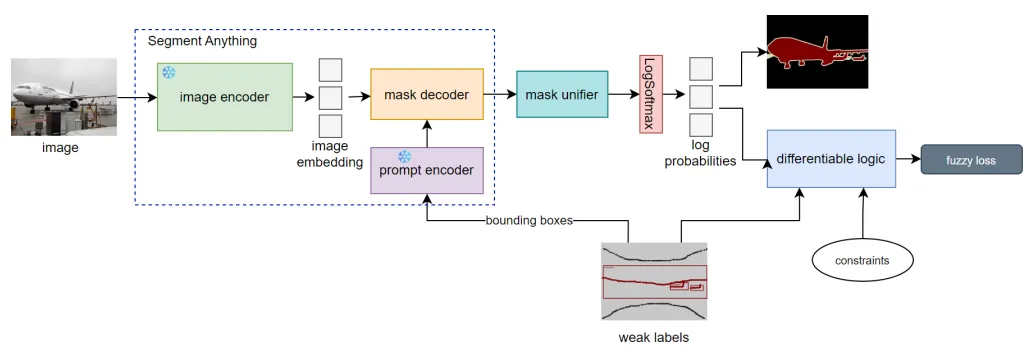
Project Overview
This project was developed as part of my Master's thesis at KU Leuven, focusing on image segmentation using weak supervision techniques.
The goal was to develop a unified framework for weakly supervised semantic segmentation, leveraging various forms of weak annotations such as scribbles, and bounding boxes, or even other background knowledge expressed as first-order logic formulas.
Key Features
- Leverages the performance of the Segment Anything Model
- Unifies learning, exploiting any type of weak labels as well as other prior knowledge, expressable as first-order logic formulas
- Achieved state-of-the-art results on Pascal VOC 2012 and LGG segmentation
Results
The proposed method achieved state-of-the-art performance on the benchmarking dataset Pascal VOC 2012, as well as in a more practical scenario - in medical image segmentation, where the method easily extends to segmenting low-grade gliomas in brain MRI scans.
Impact
The novely of this thesis is the application of logic-based reasoning to the weakly supervised segmentation task. Additionally, it is the first unified framework, supporting learning from various weak annotations and background knowledge.
The research contributes to the field of computer vision by demonstrating how weak supervision can significantly reduce annotation requirements while maintaining high segmentation accuracy. This approach has applications in various domains, including medical imaging, where annotated data is often scarce and expensive to obtain.